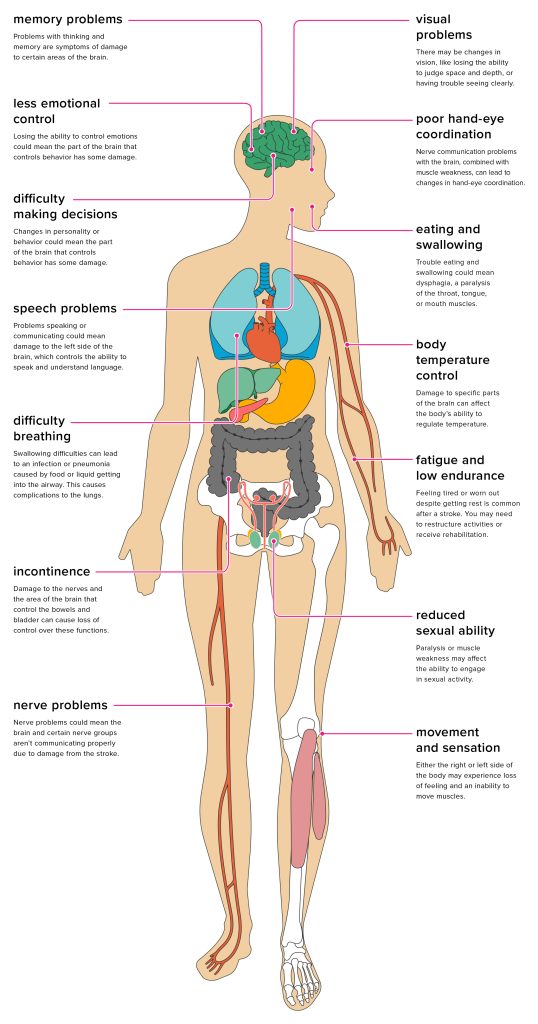
Every year, hundreds of thousands of people around the world have a stroke, and many will experience communication problems as a result.
Introduction
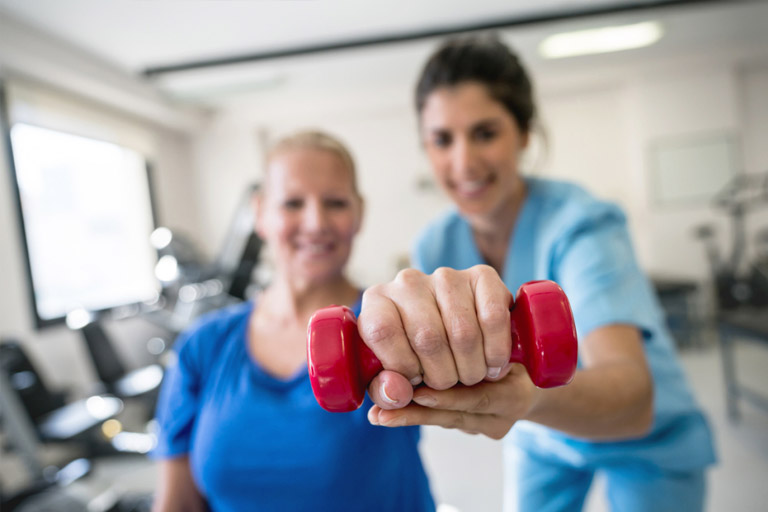
The aim of stroke recovery is to assist you in relearning skills that you might have missed as a result of a stroke that damaged a part of your brain. Rehabilitation after a stroke will help you recover your independence and improve your quality of life. Stroke complications differ in severity, as does each person’s ability to recover. People who engage in a focused stroke recovery programmer perform better, according to research.
Stroke therapy can be approached in a variety of ways. The part of your body or type of skill affected by your stroke will determine your recovery strategy.
The following are examples of physical activities: .
Exercising your motor skills: These exercises will help you strengthen your muscles and develop your coordination. It’s possible that you’ll need swallowing therapy.
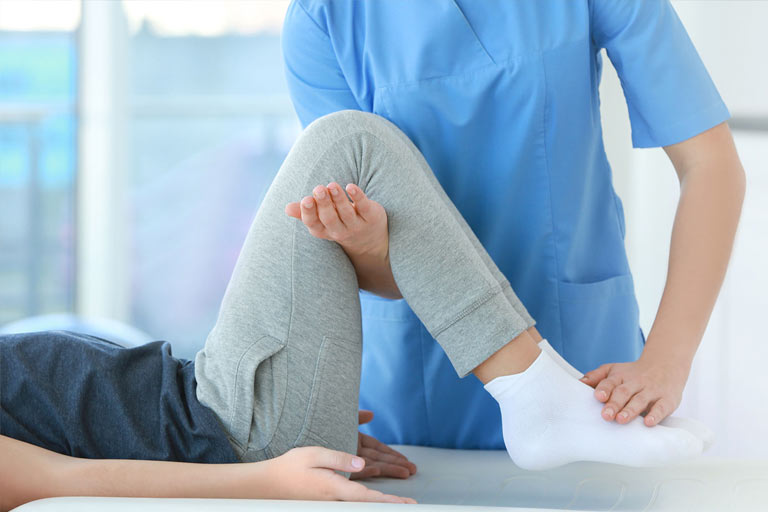
Exercise to improve mobility: You might learn to use a walker, canes, wheelchair, or ankle brace as a mobility aid. While you relearn to walk, the ankle brace will help stabilize and strengthen your ankle to help support your body’s weight.
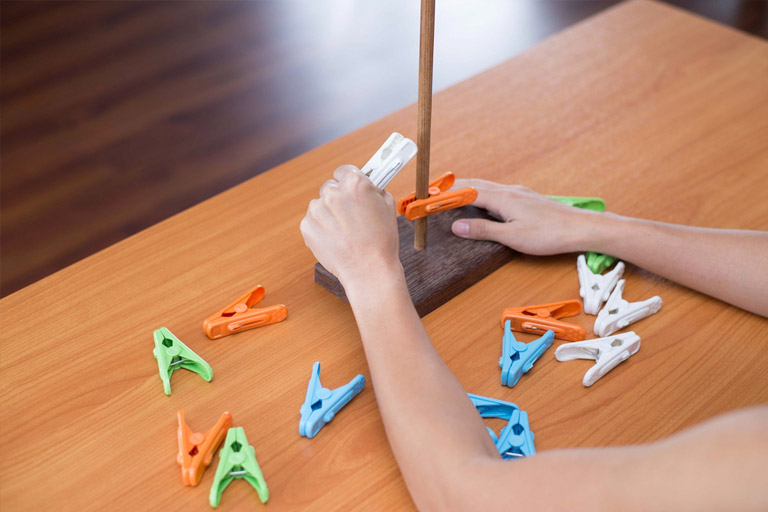
Constraint-induced therapy is a form of therapy that involves putting yourself in a situation when you practice moving the affected limb to help strengthen its function, an unaffected limb is restrained. Force therapy is a term used to describe this type of therapy.
Have a better chance of regaining lost abilities and skills if you start stroke therapy as soon as possible. Doctors’ immediate goals, on the other hand, are to:
Ensure that the medical situation remains stable.
ï?· Control potentially life-threatening situations.
ï?· Stop another stroke from happening.
ï?· Any stroke-related symptoms should be kept to a minimum.
ï?· Stroke recovery will begin as soon as 24 to 48 hours after your stroke, while you’re still in the hospital.
The duration of your stroke recovery is determined by the seriousness of your stroke and any complications that might arise. Some stroke survivors make a fast recovery. However, the majority of people will need longterm stroke recovery, which may last months or years after their stroke.
Stroke recovery requires the involvement of a number of clinicians.
Physical needs should be addressed by the following specialists:
Doctors are medical professionals. Your primary care physician, as well as neurologists and physical therapy and rehabilitation professionals, will help you navigate your treatment and avoid complications. These doctors will also assist you in developing and maintaining good lifestyle habits in order to prevent another stroke.
Nurses that specialize in rehabilitation. Nurses who specialize in caring for people who have physical disabilities will assist you in incorporating the skills you learn into your everyday routine. Rehabilitation nurses can also help with bowel and bladder problems caused by a stroke.
Physiatrists are a type of physical therapy. These therapists assist you in relearning basic movements like walking and maintaining your balance.
The time it takes to recover from a stroke varies from person to person. It’s difficult to say how many skills you’ll regain and when. In general, successful stroke recovery hinges on the following factors: Physical causes, such as the severity of the stroke in terms of cognitive and physical consequences.
Emotional factors, such as your motivation and mood, as well as your ability to adhere to recovery activities outside of counseling sessions, are all important. Support from friends and family are examples of social influences.